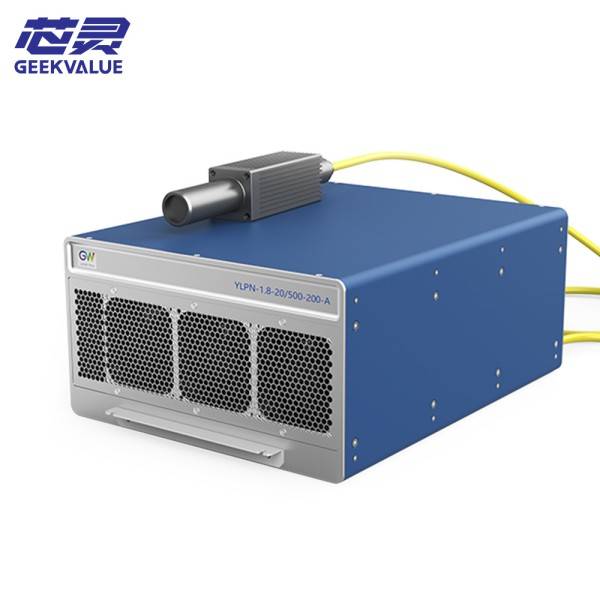
GW YLPN-1.8-2 500-200-F is a high-precision nanosecond short-pulse laser (DPSS, diode-pumped solid-state laser) produced by GWU-Lasertechnik (now part of Laser Components Group) in Germany. It is widely used in:
Industrial micromachining (PCB drilling, glass cutting)
Scientific research experiments (spectral analysis, laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy LIBS)
Medical beauty (pigmentation removal, minimally invasive surgery).
Core parameters:
Wavelength: 532nm (green light) or 355nm (ultraviolet)
Pulse width: 1.8~2ns
Repetition frequency: 500Hz~200kHz adjustable
Peak power: high energy density, suitable for precision machining.
2. Daily maintenance methods
(1) Optical system maintenance
Daily weekly inspection:
Use dust-free compressed air to clean the laser output window and reflector.
Check the alignment of the optical path (to avoid deviation caused by mechanical vibration).
Quarterly in-depth maintenance:
Use special optical cleaner + dust-free cotton swab to wipe the lens (do not use alcohol to avoid coating damage).
Detect the transmittance of the laser crystal (such as Nd:YVO₄) and replace it if necessary.
(2) Cooling system management
Coolant maintenance:
Use deionized water + anti-corrosion agent, replace every 6 months.
Check the sealing of the water pipe joint to prevent leakage.
Radiator cleaning:
Clean the dust on the air-cooled heat sink every 3 months (to ensure heat dissipation efficiency).
(3) Electrical and mechanical inspection
Power supply stability:
Monitor the input voltage fluctuation (need <±5%), it is recommended to equip with UPS voltage stabilizer.
Check whether the pump diode (LD) drive current is normal.
Environmental control:
Operating temperature 15~25°C, humidity <60%, avoid condensation.
3. Common faults and diagnosis
(1) Laser output power decreases
Possible causes:
Optical lens contamination or coating damage
Laser crystal (Nd:YVO₄/YAG) aging or thermal lens effect
Pump diode (LD) efficiency decreases.
Diagnostic steps:
Use a power meter to detect output energy.
Check the optical path in sections (isolate the resonant cavity and test the performance of a single module).
(2) Pulse instability or missing
Possible causes:
Q switch (such as acousto-optic modulator AOM) drive failure
Control circuit board (such as FPGA timing board) signal abnormality
Power module power supply is insufficient.
Diagnostic steps:
Use an oscilloscope to detect the Q switch drive signal.
Check whether the repetition frequency setting exceeds the limit.
(3) Cooling system alarm
Possible causes:
Insufficient coolant flow (water pump failure or pipe blockage)
TEC (thermoelectric cooler) failure
Temperature sensor drift.
Diagnostic steps:
Check the water tank level and filter.
Measure whether the voltage across the TEC is normal.
(4) The device cannot start
Possible reasons:
Main power supply is damaged (fuse is blown)
Safety interlock is triggered (such as the chassis is not closed)
Control software communication error.
Diagnostic steps:
Check the power input and fuse.
Restart the software and reinstall the driver.
4. Repair ideas and processes
(1) Modular troubleshooting
Optical part:
Clean or replace the contaminated lens → Recalibrate the optical path.
Electronic control part:
Replace the damaged Q switch driver board → Calibrate the pulse timing.
Cooling part:
Unblock the blocked pipeline → Replace the faulty water pump/TEC.
(2) Calibration and testing
Pulse detection: Use a high-speed photodetector + oscilloscope to verify the pulse width and stability.
Beam quality analysis: Use an M² meter to ensure that the beam divergence angle meets the standard.
(3) Spare parts selection recommendations
Original spare parts (such as LD modules and Q switches provided by GWU/Laser Components) are preferred.
Alternative: highly compatible third-party spare parts (parameter matching needs to be verified).
5. Preventive maintenance plan
Monthly: record output power and pulse parameter trends.
Every six months: optical cavity calibration by professional engineers.
Yearly: comprehensive inspection of cooling system and power module aging.
Conclusion
Through standardized daily maintenance + modular maintenance ideas, the life of YLPN lasers can be greatly extended and downtime can be reduced. If you need in-depth support, please feel free to contact our technical team